Витамин д при розацеа, Кто вылечил РОЗАЦЕА? - 26 ответа на форуме androidhub.ru () | Страница

В году упоминалось, что розацеа может быть причиной потери бровей и облысения [48]. Раздел: Активные ингредиенты. Поговаривали, что у людей с розацеа может быть повышен уровень витамина Д в крови. Там, у молодого человека тоже ушла капиллярная сетка. Хлеб ем немного я худая, без хлеба усохну , ну остальное стандартно - без остр, копчен, кислого, жирного, жареного итд.
Eur J Dermatol.

Antimicrobial peptides and wound healing: biological and therapeutic considerations. Exp Dermatol. A peptide antibiotic from human skin.

Differential expression of antimicrobial peptides in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis as a novel contributory mechanism for skin and joint disease heterogeneity. Scand J Rheumatol. Cytokine milieu of atopic dermatitis, as compared to psoriasis, skin prevents induction of innate immune response genes. J I mmunol. Dermal group 2 innate lymphoid cells in atopic dermatitis and allergy. Curr Opin Immunol. A role for IL and ILdriven type-2 innate lymphoid cells in atopic dermatitis.
J Exp Med. Deficiency of dermcidin-derived antimicrobial peptides in sweat of patients with atopic dermatitis correlates with an impaired innate defense of human skin in vivo. What is the role of antimicrobial peptides AMP in acne vulgaris? Reduced expression of dermcidin, a peptide active against propionibacterium acnes, in sweat of patients with acne vulgaris.
Acta Derm Venereol. Neutrophils activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells by releasing self-DNA-peptide complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci Transl Med. Ultraviolet A1-induced downregulation of human beta-defensins and interleukin-6 and interleukin-8 correlates with clinical improvement in localized scleroderma.
Neurovascular and neuroimmune aspects in the pathophysiology of rosacea. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc.
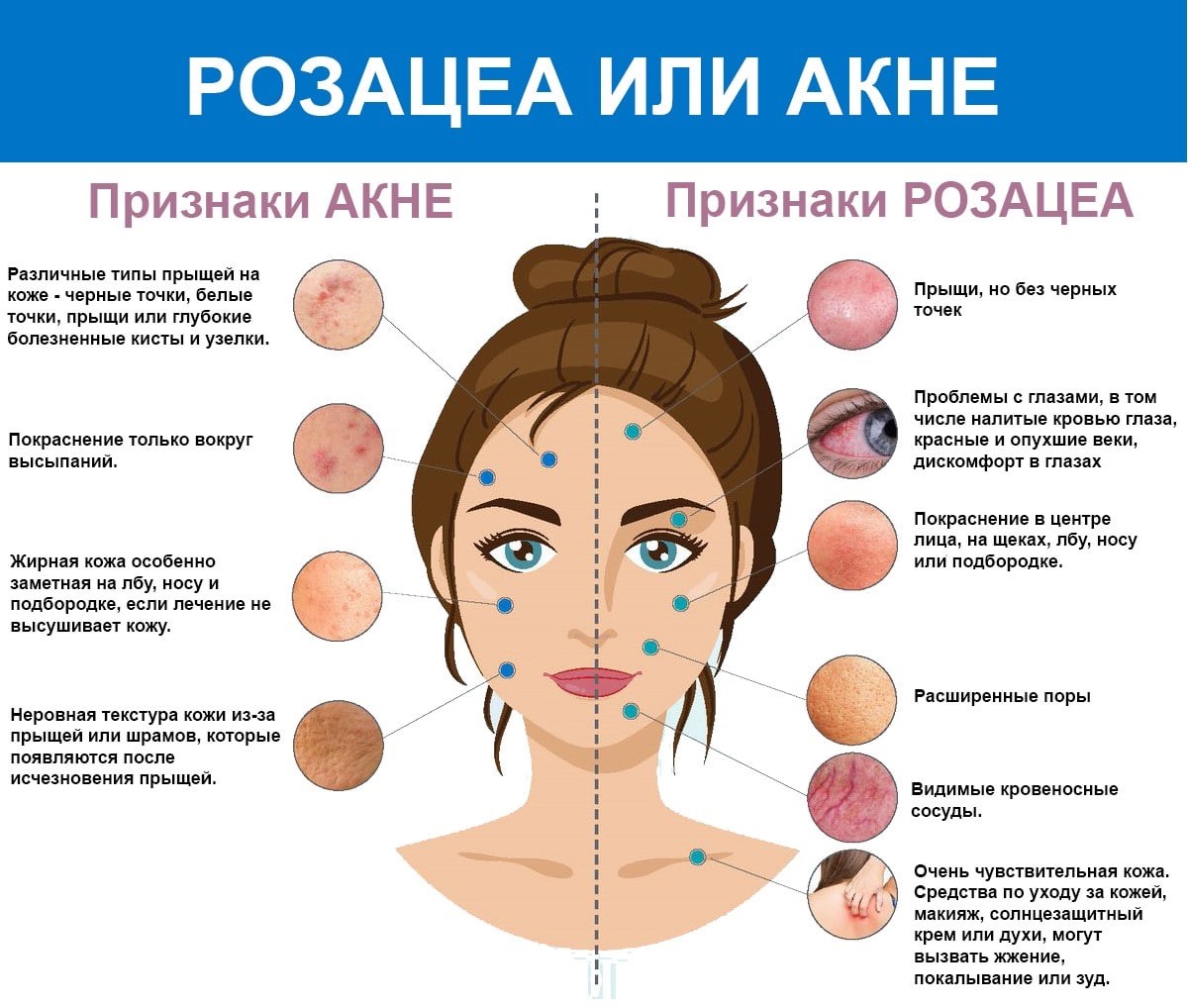
Increased serine protease activity and cathelicidin promotes skin inflammation in rosacea. Nat Med. Kallikrein 5-mediated inflammation in rosacea: clinically relevant correlations with acute and chronic manifestations in rosacea and how individual treatments may provide therapeutic benefit.
J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. Rosacea: Skin innate immunity gone awry? Vitamin D status in patients with rosacea. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide CAMP gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up-regulated in myeloid cells by 1,dihydroxy vitamin D3. Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response. Cutting edge: 1,dihydroxy vitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression J.
Rosacea: The blessing of the celts — an approach to pathogenesis through translational research. Rosacea and gastrointestinal disorders: a population-based cohort study.
Clustering of autoimmune diseases in patients with rosacea. Inflamm Bowel Dis. Friends or Foes? Host defense antimicrobial peptides and proteins in human skin diseases.
Histopathological analysis of patients with rosacea according to rosacea subtype and severity. Am J Dermatopathol. Morphology of two Demodex folliculorum hominis forms and its role in skin diseases. Authoreferat of Ph. Mite related bacterial antigens stimulate inflammatory cells in rosacea.
The role of Demodex mites in the development of papulo-pustular dermatitis. Experimentalnaya I clinicheskaya dermatocosmetologiya. Interventions for rosacea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. The proposed inflammatory pathophysiology of rosacea: implications for treatment. Activation of neutrophils via IP3 pathway following exposure to demodex-associated bacterial proteins.
Demodex-associated bacterial proteins induce neutrophil activation. Scavenging properties of metronidazole on free oxygen radicals in a skin lipid model system. J Pharm Pharmacol. Jones D. Reactive oxygen species and rosacea. Miyachi Y. Potential antioxidant mechanism of action for metronidazole: implications for rosacea management.
Adv Ther. Int Immunopharmacol. Farm Hosp. Metronidazole neurotoxicity: sequential neuroaxis involvement. Neurol India. Azelaic acid: evidence-based update on mechanism of action and clinical application. J Drugs Dermatol. Ito T. Mazzotti reaction with eosinophilia after undergoing oral ivermectin for scabies. J Dermatol. Mazzotti reaction after presumptive treatment for schistosomiasis and strongyloidiasis in a Liberian refugee.
Pediatr Infect Dis J. Complex therapy of acneform dermatoses. Experiment clin dermatocosmetol. Forgot Password? Второй момент: истончение структур кожи, в том числе и ПЖК подкожно-жировой клетчатки , из-за чего сосуды становятся видимыми.
Витамин D, наоборот, укрепляет сосудистую стенку, положительно влияет на функцию соединительной ткани. В частности, благодаря витамину D фибробластами усиливается синтез коллагена, нормализуется контакт между кератиноцитами. Кожа уплотняется, улучшается структура коллагена и эластина, подтягивается каркас лица. Витамин D способствует тому, чтобы сосуды были менее заметными. К тому же он обладает антибактериальным эффектом: снижает как местное, так и системное воспаление, улучшает состояние кожи лица.
Если сочетать мезотерапию, биоревитализацию, массаж с приемом витамина D, эффект будет значительно лучше. Если принимать витамин D вместе с коллагеном, аминокислотным коктейлем, то структура коллагена в коже существенно улучшается в сравнении с моноприемом коллагена. А на вопрос, что делать, если женщине с куперозом назначили витамин D, принимать или нет, отвечу так: конечно, принимать лучше с витамином C, рутином и другими эластопротекторами, возможно, с коллагеном.
И желательно посетить врача-косметолога, чтобы подобрать подходящие, стимулирующие фибробласты процедуры, чтобы коагулировать те сосуды, которые уже образовались, и препятствовать появлению новых. Азбука здоровья. Кинофестиваль Дух Огня.